What Is ECG and How Does It Work?
Your heart is one of the most vital organs in your body — beating continuously to pump blood, deliver oxygen, and sustain life. To ensure it’s functioning properly, medical professionals use a range of diagnostic tools, and one of the most common and effective among them is the Electrocardiogram, commonly known as ECG or EKG.
In this blog, we’ll explore what an ECG is, how it works, its benefits, uses, importance in modern healthcare, and any potential side effects you should know.
What Is an ECG?
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a simple, non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity of your heart. Every time your heart beats, it produces small electrical signals that coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles. These signals are essential to keep your heartbeat regular and efficient.
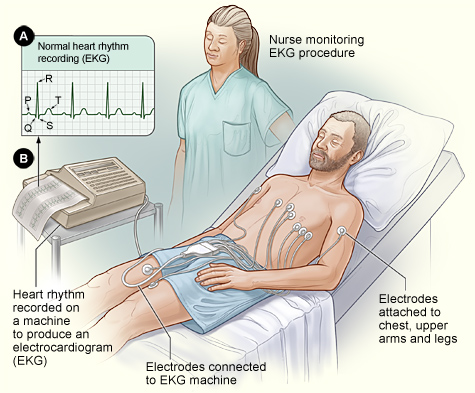
An ECG records these signals through small sensors called electrodes, which are placed on your chest, arms, and legs. The data is then displayed as a series of waves on a screen or printed paper, representing how your heart is functioning in real time.
Doctors analyze these wave patterns to identify irregularities in your heart rhythm, detect heart attacks, and monitor the effectiveness of ongoing heart treatments.
How Does an ECG Work?
The working principle of an ECG is quite straightforward, though scientifically fascinating.
-
Electrode Placement
During the procedure, a healthcare professional attaches several small, sticky electrodes to your skin — typically on the chest, wrists, and ankles. These electrodes are connected to an ECG machine using thin wires. -
Electrical Signal Detection
As your heart beats, it sends out tiny electrical impulses. The electrodes pick up these signals and transmit them to the ECG machine. -
Data Recording
The ECG device then records the signals and translates them into visual tracings — typically a line graph showing waves that correspond to each heartbeat. -
Analysis
A doctor interprets these waveforms (P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves) to determine if your heart rhythm and electrical conduction are normal or if there are signs of issues such as arrhythmia, heart blockage, or damage from a previous heart attack.
The entire process is quick, painless, and completely safe. A standard ECG usually takes about 5 to 10 minutes, and you can resume normal activities immediately afterward.
Types of ECG Tests
Depending on the symptoms and the condition being examined, there are different types of ECG tests:
-
Resting ECG: Performed while you are lying still; used for routine heart monitoring.
-
Stress ECG (Exercise ECG): Conducted while you walk or run on a treadmill to see how your heart performs under stress.
-
Holter Monitoring: A portable ECG device worn for 24–48 hours to record your heart’s activity throughout your daily routine.
Benefits of ECG
An ECG test offers numerous benefits for both preventive and diagnostic purposes:
1. Early Detection of Heart Diseases
ECGs can detect heart problems such as coronary artery disease, irregular heart rhythms, and heart attacks early — allowing timely treatment.
2. Non-Invasive and Painless
The test involves no needles, injections, or invasive procedures. It’s completely safe and comfortable for all age groups.
3. Quick and Accurate Results
The test takes only a few minutes and provides instant data, helping doctors make prompt decisions.
4. Monitoring Heart Treatments
If you are on medication or have undergone heart surgery, an ECG helps track your heart’s response to treatment.
5. Useful for Routine Check-Ups
Regular ECG testing can help prevent future complications, especially for people with a family history of heart disease.
Uses of ECG
ECG is a versatile diagnostic tool used in various medical situations. Some of its key applications include:
-
Detecting Arrhythmias: Identifying irregular or abnormal heartbeats.
-
Diagnosing Heart Attacks: Recognizing signs of a past or ongoing heart attack.
-
Evaluating Chest Pain: Determining whether chest discomfort is heart-related.
-
Checking Heart Health Before Surgery: Ensuring the heart can safely handle anesthesia and surgery.
-
Assessing Pacemaker Function: Monitoring if a pacemaker is working effectively.
-
Tracking Effects of Medications: Observing how heart-related drugs impact heart rhythm.
Importance of ECG in Modern Medicine
ECG is one of the most important tools in cardiology and general medicine because it provides real-time insights into heart health. Its importance lies in its ability to:
-
Prevent serious cardiac events: By identifying issues before they become life-threatening.
-
Support emergency care: ECG is often the first test performed when a patient experiences chest pain or fainting.
-
Aid in long-term monitoring: Continuous or periodic ECGs can track chronic conditions over time.
-
Guide treatment decisions: ECG data helps doctors customize medication plans, surgeries, or lifestyle changes for better outcomes.
With heart disease being one of the leading causes of death worldwide, the role of ECG in early detection and prevention cannot be overstated.
Are There Any Side Effects of ECG?
An ECG test is extremely safe and has no major side effects. However, some people may experience:
-
Mild Skin Irritation: From the adhesive electrodes, especially for those with sensitive skin.
-
Discomfort from Cold Electrodes: Electrodes or gel might feel cold during application.
-
Temporary Redness: A slight mark or redness may appear where electrodes were placed, but it fades quickly.
These are minor and temporary. The test itself does not emit any electricity into your body — it only records existing signals — so there is no risk of shock or pain.
Who Should Get an ECG?
You may be advised to get an ECG if you experience:
-
Chest pain or pressure
-
Shortness of breath
-
Dizziness or fainting
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
-
Unexplained fatigue
-
Family history of heart disease
It’s also recommended for older adults, people with diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or those leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Conclusion
An ECG (Electrocardiogram) is one of the most reliable, safe, and effective tools for assessing heart health. It helps detect potential problems early, monitor existing conditions, and ensure that your heart is functioning optimally.
Whether as part of a routine check-up or a diagnostic test, an ECG provides vital information that could save your life. If you experience any heart-related symptoms or simply want to stay proactive about your health, don’t hesitate to schedule an ECG test.
Your heart works tirelessly for you — give it the care and attention it deserves.